How Much Beef Do Americans Eat Yearly
Burgers, bacon, steaks, and other meat products have come nether scrutiny in recent years due to their bear upon on health, sustainability, and social justice issues. The number of companies working on meat alternatives in the U.Due south. is growing. One-half of U.Southward. consumers nether the age of 50 accept already tried a institute-based meat product. Yet meat consumption in the U.South. is on the ascent. As of 2017, America had the 2d-highest meat consumption in the globe, surpassed but by Hong Kong. How much meat do Americans eat, and what are the impacts of their meat consumption?
How Much Meat Is Consumed in the U.Southward.?
Americans eat around 274 pounds of meat per year on boilerplate, not accounting for seafood and fish, or individual food waste material. The full corporeality of meat consumed in the U.S. has increased past 40 percent since 1961. In 2017, the U.Southward. Department of Agriculture (USDA) reported that Americans are exceeding the amount of meat recommended by national dietary guidelines, although women in the U.South. consume about a third less meat than men, and around 42 percent less beef.
Beef and Veal
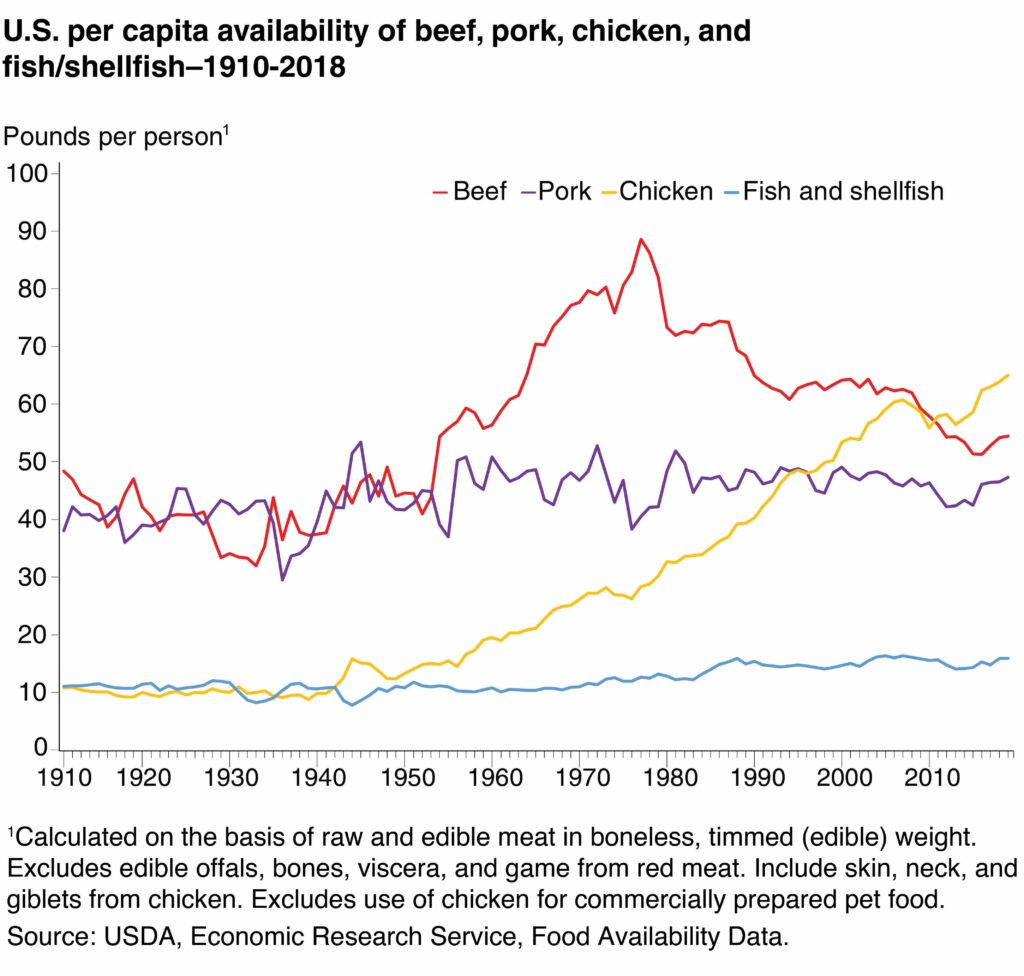
The U.S. has the world'south second-highest consumption of beefiness and buffalo after Argentina. In 2017 Americans consumed 81.74 pounds of beefiness and buffalo per capita, a 37 per centum decrease from 1976, when Americans had reached a tape consumption of 129.65 pounds per capita. In the late 1970s beef consumption started falling, due to scientific findings concerning the health impacts of saturated fats. In 2013 beef and buffalo consumption in the U.S. had dropped to under 80 pounds per capita, just then started rising again.
Pork
Pork consumption in the U.S. fluctuated betwixt 72.64 and 53.nineteen pounds per capita between 1961 and 2017. The latest data shows that Americans eat an annual 66.eighteen pounds of pork per capita. The U.Southward. Census information and Simmons National Consumer Survey (NHCS) establish that 268 1000000 Americans ate salary in 2020, with over sixteen million eating five pounds of bacon or more during the year.
Poultry
Poultry is divers every bit domestic fowl, including chickens, turkeys, and geese. In 2017 Americans consumed a record 122.75 pounds of poultry per capita. According to the USDA, chicken consumption has increased by 540 percent since 1910, from effectually 10.i pounds per capita to 65.2 pounds in 2018. Since 1961 the consumption of poultry has more than tripled.
The growing popularity of chicken in the U.S. is linked to beefiness falling out of favor. For decades, consumers have been choosing craven over beef due to wellness and ecology concerns; yet, eating farmed chickens has too been shown to exist problematic for several reasons.
Lamb
Since the 1960s the consumption of lamb and mutton in the U.South. has fallen from almost five pounds to about ane pound per capita. Near 20 per centum of lamb consumption in the U.South. occurs during the spring holidays. Urban consumers are more likely to consume lamb than consumers based in rural areas.
What Is the Most Consumed Meat in the U.South.?
Over the last three decades, craven overtook beefiness and pork to get the most commonly consumed meat production in the U.Due south. In 2020 Americans ate 96.iv pounds of broiler chickens per capita. According to data by the USDA and Economic Research Service, Americans are expected to swallow 101.one pounds of broiler chickens per capita by 2030.
Is Meat Consumption Increasing or Decreasing?
Meat consumption in the U.S. increased by xl percent between 1961 and 2017. Globally, meat consumption increased by 58 percent between 1998 and 2018.
U.S. meat consumption is expected to increase by one per centum each year through 2023, according to the contempo Packaged Facts report Global Meat & Poultry Trends. While consumption of broiler chickens and pork is expected to rise, Americans are expected to swallow slightly smaller amounts of beef and turkey past 2030.
Is the Meat Industry Dying?
The number of Americans identifying every bit vegetarians has remained roughly the same at six percent since 1999, according to Gallup surveys. The number of self-identifying vegans increased from just 2 to three percentage between 2012 and 2018. Nonetheless, and despite projections of growing meat consumption, 23 percent of Americans reported reducing the corporeality of meat they ate in 2019. The number of U.S. consumers who have tried plant-based alternatives has also risen to lxx pct.
Investment house UBS predicts that annual sales in the institute-based meat market place will grow from $four.half dozen billion in 2018 to $85 billion in 2030. According to global consultancy AT Kearney, threescore percent of meat eaten globally in 2040 volition be from plant-based or lab-grown alternatives. In response to irresolute consumer preferences, traditional meat producers are increasingly adding plant-based alternatives to their product ranges. A 2021 report found that the average American believes that the U.S. could get completely plant-based by 2039. Nonetheless when faced with falling local demand, some meat companies instead resort to increasing their exports to countries with rising meat consumption levels. In September 2020, for example, the U.South. pork manufacture exported a record 29 pct of full pork production to buyers exterior the U.S.
How Much Meat Is Wasted in the U.S.?
According to a 2020 study, Americans waste product effectually a 3rd of the food they purchase, costing the average household $i,866 per yr, or $240 billion for the whole population. Fresh meat requires processing, and is a highly perishable product, which increases the likelihood of waste matter.
The USDA estimates that only half of the torso of a slaughtered cow, hog, lamb, chicken, or turkey ends up being eaten. Beef, for case, tin be wasted equally it moves from subcontract to retail due to damage during packaging, inadequate storage, or when inspectors reject information technology for safety reasons. Within retail, packaging failures, color changes, spoilage, and overstocking can all cause farther loss. At the consumer level beefiness can be wasted due to inadequate storage, spoilage, recalls, and when consumers set more beefiness than they ultimately swallow.
Taking the number of farmed animals who die before slaughter into business relationship, the amount of meat wasted in the U.S. is even higher. Co-ordinate to Iowa Land Academy, an estimated 1 out of three pigs born into the U.S. pork manufacture dies earlier slaughter.
Meat waste entails wasting the land, feed, water, labor, antibiotics, and equipment needed to raise animals from nascency to slaughter. Farmed animals only convert two to 13 percent of the calories they eat into edible body parts. Poultry wastes 77 per centum of feed calories, pork 91 percent, lamb and mutton 94 percent, and beef 98 pct.
When nosotros recognize the resources-intensiveness of animal agronomics, we can meet meat consumption itself as a form of food waste.
What Would Happen If Everyone Ate Less Meat?
Animal agriculture, including meat product, is responsible for at least 37 pct of all greenhouse gas emissions. Increasing global meat consumption pushes the planet closer to dangerous limits. Supposing that the whole world adopted the U.Due south. diet, 138 percentage of the world's habitable land, more land than is available, would be required to meet homo dietary needs. If the world instead adopted the more than found-based diet(s) of Bharat, the area of habitable state currently used for agronomics could be more than than halved, from l to 22 percent.
Reducing meat consumption and transitioning to more establish-based diets would prevent further deforestation, biodiversity loss, and environmental pollution; improve global wellness, including lowering the risk of zoonotic outbreaks and antibiotic resistance; reduce greenhouse gas emissions; and free upwards a large amount of land, which could be used for reforestation. If the entire U.S. population switched from beef to beans, 42 percent of U.S. cropland—267,537 square miles—could be repurposed for the restoration of ecosystems and more climate-friendly farming.
Plant poly peptide tin replace creature protein to meet human dietary needs. Instead of monocultures used to grow brute feed, farmers could repurpose land to grow more various crops, such as vegetables and pulses. Pulses have nitrogen-fixing properties, are a healthy source of protein with a long shelf life, and can significantly ameliorate soil fertility and reduce food loss in agriculture.
Eating Less Meat
Meat consumption in the U.Due south. remains high, despite the increasingly urgent need to change global eating habits. Beast products have a significantly larger environmental footprint than establish-based products. According to scientists, a plant-based diet is "probably the single biggest manner to reduce your impact on planet Globe."
Since U.S. citizens have one of the highest rates of meat consumption globally, more people eating a found-based diet is critical to reducing the land'southward emissions, and transitioning towards a more sustainable organization of food production.
Source: https://sentientmedia.org/meat-consumption-in-the-us/
0 Response to "How Much Beef Do Americans Eat Yearly"
Post a Comment